Small-scale Home/Office Secure Energy Management based on Individual Power Consumption Data Analysis
Sustainable energy use requires optimal energy utilisation within smart grid systems. By empowering the Internet of Things (IoT) based wireless connectivity, through real-time energy monitoring and power consumption patterns analysis, IoT based networks can collect data from appliances and devices in the home or office; thus helping us understand power consumption patterns for individuals. This research can be used to inform end-users to adapt their behaviours and patterns for a variety of energy efficiency benefits.
Project Objectives
- Build low-cost, flexible wireless architecture and networks at homes and offices to collect power consumption data.
- Label the power consumption data from smart plugs and analyse usage patterns.
- Develop a framework based on behaviour analysis, to guide users to smart energy consumption.
Methodology
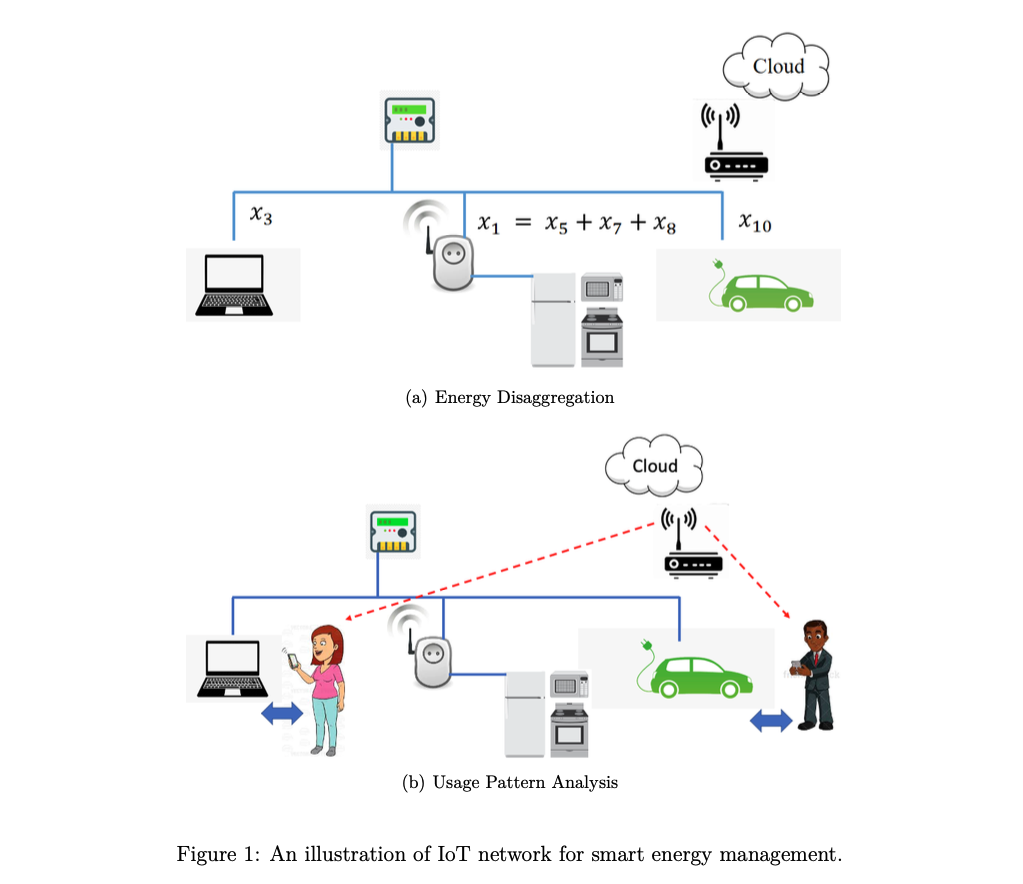
Wireless IoT technology coupled with smart plugs/smart meters to connect low-cost, small-scale office workspaces for personal power consumption management, including real-time monitoring of energy consumption, analysing power usage patterns and recognising the resident’s electricity consumption behaviours.
Machine Learning Models were trained for real-time energy disaggregation in the local home server. Simultaneously, the local data was regularly uploaded to the cloud server for usage patterns analysis. After combining other information (e.g., electricity price and personal information), the system provides intelligent services (e.g., recommendations) for end-users.
Research Goal
The research goal was to address the challenge of one-to-one mapping of energy disaggregation in device-sharing environments by multi-users, aiming to accurately match the energy consumption of electrical appliances with specific users. It differs from existing studies on power consumption analysis for the whole household. The significance includes helping reduce individual power consumption in the small-scale IoT network (e.g. homes and offices) and benefits the large-scale IoT network (e.g. buildings, communities, and widespread regions) in total energy savings.
Categories: Major Projects